[ad_1]
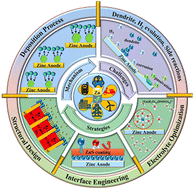
Rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) have attracted important consideration in large-scale vitality storage techniques as a consequence of their distinctive deserves, equivalent to intrinsic security, low value, and comparatively excessive theoretical vitality density. Nevertheless, the dilemma of the uncontrollable Zn dendrites, extreme hydrogen evolution response (HER), and aspect reactions that happen on the Zn anodes have hindered their commercialization. Herein, a state-of-the-art overview of the rational design of extremely reversible Zn anodes for high-performance AZIBs is offered. Firstly, the basic understanding of Zn deposition, with regard to the nucleation, electro-crystallization, and development of the Zn nucleus is systematically clarified. Subsequently, a complete survey of the vital components influencing Zn plating along with the present primary challenges is introduced. Accordingly, the rational methods emphasizing structural design, interface engineering, and electrolyte optimization have been summarized and analyzed intimately. Lastly, future views on the remaining challenges are beneficial, and this overview is anticipated to make clear the long run improvement of steady Zn anodes towards high-performance AZIBs.
[ad_2]