[ad_1]
A novel two-dimensional (2D) nanoconfinement method has been proposed to enhance the oxygen evolution response (OER) exercise of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with low conductivity. The outcomes of the research have been revealed within the journal Nature Communications.
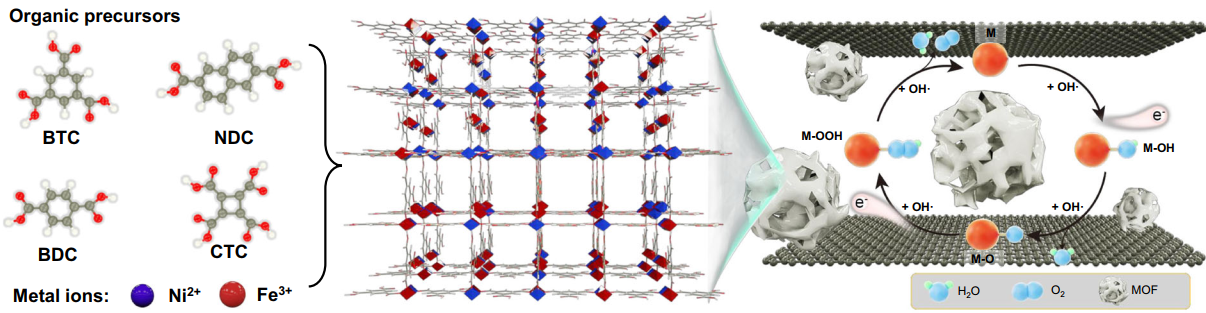
The as-prepared NiFe-MOF//G by way of the nanoconfinement from graphene multilayers. Picture Credit score: Ningbo Institute of Supplies Know-how and Engineering (NIMTE)
This novel method was put collectively by Professor Zhang Tao’s group on the Ningbo Institute of Supplies Know-how and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences (CAS), in partnership with Professor Xiao Jianping from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of CAS and Professor Hou Yang from Zhejiang College.
The progress of extremely efficient electrocatalysts for the electrochemical altering of water to supply eco-friendly and sustainable hydrogen power has garnered growing consideration over the a long time. Regardless of the essential function the OER performs in water splitting, OER on the anode eagers for a excessive thermodynamic potential to speed up water splitting kinetics.
As a result of giant floor space, numerous compositions, tunable porosity, and metallic facilities, MOFs have risen as potential candidates for extremely efficient OER electrocatalysts. Nevertheless, the innate poor conductivity of a majority of MOFs obstructs their catalytic efficiency.
To resolve this downside, scientists at NIMTE instructed an electrochemical method to restrain MOFs between graphene multilayers by way of the two-electrode electrochemical system, thereby bestowing poorly conductive MOFs with robustly improved catalytic efficiency.
The as-prepared NiFe-MOF//G shows an unusually low overpotential of 106 mV to increase to 10 mA cm-2, exceeding the unique NiFe-MOF and different beforehand recorded MOFs and their derivatives. Furthermore, the NiFe-MOF//G electrode is very steady and might maintain the efficiency for over 150 h at 10 mA cm-2 with out noticeable exercise decline.
The outcomes of X-Ray absorption spectroscopy exams and density-functional idea calculations present that the nanoconfinement from graphene multilayers improves the digital construction and catalysis middle of MOF supplies with the event of extraordinarily reactive NiO6-FeO5 distorted octahedral species in MOF construction.
Moreover, the nanoconfinement minimizes the restrictive potential for the water oxidation response.
The nanoconfinement method might be utilized to different numerous MOFs with varied constructions, considerably enhancing their electrocatalytic performances. This research challenges the prevalent thought of authentic MOFs as inert catalysts and exposes the limitless software prospects of poorly conductive and even insulating MOFs for electrocatalysis functions.
Journal Reference
Lyu, S., et al. (2022) Distinctive catalytic exercise of oxygen evolution response by way of two-dimensional graphene multilayer confined metal-organic frameworks. Nature Communications. doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33847-z.
Supply: https://english.cas.cn
[ad_2]
