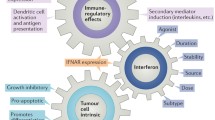
Abstract
Since their introduction to the clinic some 30 yr ago, interferons (IFNs) have become standard therapy for a range of disorders, including malignant and benign tumors as well as various viral diseases. Although IFNs will induce remissions in some patients with cancer, they are of no benefit or, at best, lead only to minor improvements in the great majority of patients with malignant disease. One of the great challenges of IFN research is to understand the multiple ways by which IFNs influence the behavior of tumor cells and to identify the factors that underlie the resistance of some tumors to IFNs. This reviews is written with a focus on two anticellular effects of IFN, inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis, possible mechanisms underlying the antitumor action of IFN. In addition, possible reasons for IFN tumor cell resistance are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Mayer, E. and De Mayer-Guiginard, J. (1998). Interferons and Other Regulatory Cytokines, Wiley, New York.
Ihle, J.N. (1996). STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell 84:331–334.
Strander, H. and Cantell, K. (1966). Production of interferon by human leukocytes in vitro. Ann. Med. Exp. Fenn. 44:265–273.
Einhorn, S. and Strander, H. (1993). Interferon treatments of human malignancies—a short review. Med. Oncol. Tumor Pharmacother. 10:25–29.
Grandér, D., Öberg, K., Lundqvist, M.L., Janson, E.T., Erksson, B. and Einhorn, S. (1990). Interferon-induced enhancement of 2′,5′ oligoadenylate synthetase in mid-gut carcinoid tumors. Lancet 336:337–339.
Gresser, I., Maury, C. and Brouty-boyé, D. (1972). Mechansim of the antitumor effect of interferon in mice. Nature 239:167–168.
Gresser, I., Kaido, T., Maury, C., Woodrow, D., Moss, J. and Belardelli, F. (1994). Interaction of IFNα/β with host cells essential to the early inhibition of Friend erythroleukemia visceral metastases in mice. Int. J. Cancer 57:604–611.
Einhorn, S., Ahre, A., Blomgren, H., Johansson, B., Mellstedt, H. and Strander, H. (1982). Interferon and natural killer cell activity in multiple myeloma. Lack of correlation between interferon-induced enhancement of natural killer cell activity and clinical response to human interferon-α. Int. J. Cancer 30:167–172.
Håkansson, A., Gustafsson, B., and Krysander, I. (1996). Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in malignant melanoma and response to interferon alpha treatment. Br. J. Cancer 74:670–676.
Grandér, D. (1998). How do mutated oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes cause cancer? Med. Oncol. 15:20–26.
Waldman, T., Zhang, Y. and Dillehay, L. (1997). Cell-cycle arrest versus cell death in cancer therapy. Nature Med. 3:1034–1036.
Kerr, J.F., Wyllie, A.H. and Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 26:239–257.
Kolenko, V.M., Uzzo, R. G., Bukowski, R. and Finke, J.H. (2000). Caspase-dependent and -independent death path-ways in cancer therapy. Apoptosis 5:17–20.
Halestrap, A.P., Doran, E., Gillespie, J.P. and O’Toole, A. (2000) Mitochondria and cell death. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 28:170–177.
Nicholson, D.W. and Thornberry, N.A. (1997). Caspases: killer proteases. TIBS 22:299–306.
Wyllie, A.H. (1997). Apoptosis and cacinogenesis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 73: 189–197.
Le, J., Yip, Y.K. and Vilcek, J. (1984). Cytolytic activity of interferon-gamma and its synergism with 5-fluorouracil. Int. J. Cancer. 34:495–500.
Sangfelt, O., Erickson, S., Castro, J., Heiden, T., Einhorn, S. and Grander, D. (1997). Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell growth are independent responses to IFN-α. Cell Growth Diff. 8:343–352.
Grandér, D., Xu, B. and Einhorn, S. (1993). Cytotoxic effect of interferon on primary tumor cells. Studies in various malignancies. Eur. J. Cancer 14:1940–1943.
Rodriguez-Villanueva, J. and Mcdonnell, T.J. (1995). Induction of apoptotic cell death in non-meanoma skin cancer by interferon-alpha. Int. J. Cancer 61:110–114.
Deiss, L.P., Feinstein, E., Berissi, H., Cohen, O. and Kimchi, A. (1995). Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase and a novel 15-kD protein as potential mediators of the γ interferon-induced cell death. Genes Dev. 9:15–30.
Jewell, A.P., Worman, C.P., Lydyard, P.M., Yong, K.L., Giles, F.J. and Goldstone, A.H. (1994). Interferon-α up-regulates bcl-2 expression and protects B-CLL cells from apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Br. J. Haematol. 88:268–274.
Milner, A.E., Grand, R.J. and Gregory, C.D. (1995). Effects of interferon-α on human B-cells: repression of apoptosis and prevention of cell growth are independent responses of Burkitt lymphoma cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 61:348–354.
Liu, P., Oken, M., Van Ness, B. (1999). Interferon-alpha protects myeloma cell lines from dexamethosone-induced apoptosis. Leukemia 13: 473–480.
Sangfelt, O., Einhorn, S., Björklund, A.C., Wiman K.G., Okan, I. and Grander, D. (1996). Wild-type p53-induced apoptosis in a Burkitt lymphoma cell line is inhibited by interferon-γ. Int. J. Cancer 67:106–112.
Brenning, G., Jernberg, H., Gidlund, M., Sjöberg, O. and Nilsson, K. (1986). The effect of alpha and gamma-interferon on proliferation and production of IgE and beta 2-microglobulin in the human myeloma cell line U-266 and in an alpha-interferon resistant U-266 subline. Scand. J. Haematol. 37:280–288.
Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. and Rozengurt, E. (1985). Interferons as regulators of cell growth and differentiation, in Interferons, Their Impact in Biology and Medicine (J. Taylor-Papadimitriou, ed.), p. 81. Oxford Medical, Oxford.
Cuff, S. and Ruby, J. (1996). Evasion of apoptosis by DNA viruses. Immunol. Cell Biol. 74:527–537.
Zhou, A., Paranjape, J., Brown, T.L., Nie, H., Naik, S., Dong B., et al. (1997). Interferon action and apoptosis are defective in mice devoid of 2′,5′-oligoadenylate-dependent RNase L. EMBO J. 16:6355–6363.
Castelli, J.C., Hassel, B.A., Wood, K.A., Li, X.L., Amemiya, K., Dalakas, M.C., et al. (1997). A study of the interferon antiviral mechanism: Apoptosis activation by the 2–5A system. J. Exp. Med. 186:967–972.
Lee, S.B. and Esteban, M. (1994). The interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induces apoptosis. Virology 199:491–496.
Lee, S.B., Rodriguez, D., Rodriguez, J.R. and Esteban, M. (1997). The apoptosis pathway triggered by the interferon-induced protein protein kinase PKR requires the third basic domain, initiates upstream of Bcl-2, and involves ICE-like proteases. Virology 231:81–88.
Tamura, T., Ishihara, M., Lamphier, M.S., Tanaka, N., Oishi, I., Aizawa, S., et al. (1995). An IRF-1-dependent pathway of DNA damage-induced apoptosis in mitoge-activated T-lymphocytes. Nature 376:596–599.
Kumar, A., Commane, M., Flickinger, T.W., Horvath, C.M. and Stark, G.R. (1997). Defective TNF-α-induced apoptosis in STAT1-null cells due to low constitutive levels of caspases. Science 278:1630–1632.
Nagata, S. (1997). Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 88:355–365.
Selleri, C., Sato, T., Del Vecchio, L., Luciano, L., Barrett, A.J., Rotoli, B., et al. (1997). Involvement of Fas-mediated apoptosis in the inhibitory effects of interferon-α in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 89:957–964.
Dai, C.H., Price, J.O., Brunner, T. and Krantz, S.B. (1998). Fas ligand is present in human erythroid colony-forming cells and interacts with Fas induced by interferon γ to produce erythroid cell apoptosis. Blood 91:1235–1242.
Spets, H., Georgii-Hemming, P., Siljason, J., Nilsson, K. and Jernberg-Wiklund, H. (1998). Fas/APO-1 (CD95)-mediated apoptosis is activated by interferon-gamma and interferon-alpha in interleukin 6 (IL-6)-dependent cel IL-6-independent multiple myeloma cell lines. Blood 92:2914–2923.
Dai, C.H. and Sanford, B.K. (1999). Interferon γ induces upregulation and activation of caspases 1, 3, and 8 to produce apoptosis in human erythroid progenitor cells. Blood 93:3309–3316.
Deiss, L.P. and Kimchi, A. (1991). A genetic tool used to identify thioredoxin as a mediator of a growth inhibitory signal. Science 252:117–120.
Cohen, O., Feinstein, E. and Kimchi, A. (1997). DAP-kinase is a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent, cytoskeletal-associated protein kinase, with cell death-inducing functions that depend on its catalytic activity. EMBO J. 16:998–1008.
Inbal, B., Cohen, O., Polak-Charcon, S., Kopolovic, J., Vadai, E., Eisenbach, L., et al. (1997). DAP kinase links the control of apoptosis to metastasis. Nature 390:180–184.
Cohen, O., Inbal, B., Kissil, J.L., Raveh, T., Berissi, H., Spivak-Kroizaman, T., et al. (1999). DAP-kinase participates in TNF-alpha-and Fas-induced apoptosis and its function requires the death domain. J. Cell Biol. 146:141–148.
Haas-Kogan, D.A., Kogan, S.C., Levi, D., Dazin, P., T’Ang, A., Fung, Y.K., et al. (1995). Inhibition of apoptosis by the retinoblastoma gene product. EMBO J. 14:461–472.
Evan, G.I., et al. (1992). Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts Myc-myc protein. Cell 69:119–128.
Berry, D.E., Lu, Y., Schmidt, B., Fallon, P.G., O’Connell, C., Hu, S.X., et al. (1996). Retinoblastoma protein inhibits IFN-gamma induced apoptosis. Oncogene 12:1809–1819.
Pardee, A.B. (1974). A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71:1286–1290.
Grana, X. and Reddy, E.P. (1995). Cell cycle control in mammalian cells: role of cyclin, cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs), growth suppressor genes and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs). Oncogene 11:211–219.
Morgan, D.O. (1995). Principles of CDK regulation. Nature 374:131–134.
Sherr, C.J. and Roberts, J.M. (1995). Inhibitors of mammalian G1-cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 9:1149–1163.
Nevins, J.R. (1992). E2F: A link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science 258:424–429.
Paucker, G., Cantell, K. and Henle, W. (1962). Quantitative studies on viral interference in suspended L cells III. Effect of interfering viruses and interferon on the growth rate of cells. Virology 17:324–334.
Brenning, G., Åhre, A. and Nilsson, K. (1985). Correlation between in vitro and in vivo sensitivity to human leukocyte interferon in patients with multiple myeloma. Scand. J. Haematol. 35:543–549.
Heyman, M., Grander, D., Bröndum-Nielsen, K., Cederblad, B., Liu, Y., Xu, B., et al. (1994). Interferon system defects in malignant T-cells. Leukemia 8:425–434.
Roos, G., Leanderson, T. and Lundgren, E. (1984). Interferoninduced cell cycle changes in human hematopoietic cell lines and fresh leukemic cells. Cancer Res. 44:2358–2362.
Balkwill, F. and Taylor-Papdimitriou, J. (1978). Interferon affects both G1 and S+G2 in cells stimulated from quiescence to growth. Nature 274:798–800.
Tiefenbrun, N., Melamed, D., Levy, N., Resnitzky, D., Hoffman, I., Reed, S.I., et al. (1996). Alpha interferon suppresses the cyclin D3 and Cdc25A genes, leading to a reversible G0-like arrest. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:3934–3944.
Sangfelt, O., Erickson, S., Castro, J., Heiden, T., Gustafsson, A., Einhorn, S., et al. (1999). Molecular mechansims underlying interferon-α-induced G0/G1 arrest: CKI-mediated regulation of G1 Cdk-complex and activation of pocket proteins. Oncogene 18:2798–2810.
Kimchi, A. (1992). Cytokine triggered molecular pathways that control cell cycle arrest. J. Cell Biochem. 50:1–9.
Thomas, N.S., Pizzey, A.R., Tiwari, S., Williams, C.D. and Yang, J. (1998). p130, p107, and pRb are differentially regulated in proliferating cells and during the cell cycle arrest by alpha-interferon. J. Biol. Chem. 273:23,659–23,667.
Furukawa, Y., Iwase, S., Kikuchi, J., Nakamura, M., Yamada, H. and Matsuda, M. (1999). Transcriptional repression of the E2F-1 gene by interferon-alpha is mediated through induction of E2F-4/pRb and E2F-4/p130 complexes. Oncogene 18:2003–2014.
Sangfelt, O., Erickson, S., Einhorn, S. and Grander, D. (1997). Induction of Cip/Kip and Ink4 cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors by interferon-α in hematopoietic cell lines. Oncogene 14:415–423.
Hobeika, A.C., Subramaniam, P.S. and Johnson, H.M. IFN-alpha induces the expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 14:1165–1170.
Harvat, B.L., Seth, P. and Jetten, A.M. (1997). The role of p27Kip1 in gamma interferon-mediated growth arrest of mammary epithelial cells and related defects in mammary carcinoma cells. Oncogene 17:2111–2122.
Mandal, M., Bandyopadhyay, D., Goepfert, T.M. and Kumar, R. (1998). Interferon-alpha induces expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21WAF1 and p27KIP1 that prevent activation of cyclin-dependent kinase by CDK-activating kinase (CAK). Oncogene 16:217–225.
Matsoka, M., Kenzaburo, T. and Shigetaka, A. (1998). Interferon-alpha-induced G1 phase arrest through up-regulated expression of CDK inhibitors p19Ink4D and p21Cip1 in mouse macrophages. Oncogene 16:2075–2086.
Polyak, K., Kato, J.Y., Solomon, M.J., Sherr, C.J., Massague, J., Roberts, J.M., et al. (1994). p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 8:9–22.
Kato, J.Y., Matsuoka, M., Polyak, K., Massague, J. and Sherr, C.J. (1994). Cyclic AMP-induced G1 phase arrest mediated by an inhibitor (p27Kip1) of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 activation. Cell 79:487–496.
Chin, Y.E., Kitagawa, M., Su, W.C., You, Z.H., Iwamoto, Y. and Fu, X.Y. (1996). Cell growth arrest and induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 mediated by STAT1. Science 272:719–722.
Bromberg, J.F., Horvath, C.M., Wen, Z., Schreiber, R.D. and Darnell, J.E., Jr. (1996). Transcriptionally active STAT1 is required for the antiproliferative effects of both interferon alpha and interferon gamma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:7673–7678.
Ward, A.C., Touw, I. and Yoshimura, A. (2000). The JAKSTAT pathway in normal and perturbed hematopoiesis. Blood 95:19–29.
Yamaoka, T., Yano, M., Idehara, C., Yamada, T., Tomonari, S., Moritani, M., et al. (1999). Apoptosis and remodeling of beta cells by paracrine interferon-gamma without insulitis in transgenic mice. Diabetologia 42:566–573.
Xaus, J., Cardo, M., Valledor, A.F., Soler, C., Lloberas, J. and Celada, A. (1999). Interferon gamma induces the expression of p21 waf1 and arrests macrophage cell cycle, preventing induction of apoptosis. Immunity 11:103–113.
Chong, K.L., Feng, L., Schappert, K., Meurs, E., Donahue, T.F., Friesen, J.D., et al. (1992). Human p68 kinase exhibits growth suppression in yeast and homology to the translational regulator GCN2. EMBO J. 11:1553–1562.
Salzberg, S., Wreschner, D.H., Oberman, F., Panet, A. and Bakhanashvili, M. (1983). Isolation and characterization of an interferon-resistant cell line deficient in the induction of (2′,5′) oligoadenylate synthetase activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3:1759–1765.
Hassel, B.A., Zhou, A., Sotomayor, C., Maran, A. and Silverman, R.H. (1993). A dominant negative mutant of 2–5-A-dependent RNaseL suppresses antiproliferative and antiviral effects of interferon. EMBO J. 12:3297–3304.
Kirchhoff, S., Koromilas, A.E., Schaper, F., Grashoff, M., Sonenberg, N. and Hauser, H. (1995). IRF-1 induced cell growth inhibition and interferon induction requires the activity of the protein kinase PKR. Oncogene 11:439–445.
Gutterman, J.U. and Choubey, D. (1999). Retardation of cell proliferation after expression of p202 accompanies an increaase in p21 (WAF1/CIP1). Cell Growth Diff. 2:93–100.
Einat, M., Resnitzky, D. and Kimchi, A. (1985). Inhibitory effects of interferon on the experssion of genes regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:7608–7612.
Erickson, S., Sangfelt, O., Castro, J., Heyman, M., Einhorn, S. and Grander, D. (1999). Interferon-alpha inhibits proliferation in human T-lymphocytes by abrogation of IL-2 induced changes in cell cycle regulatory proteins. Cell Growth Diff. 10:575–582.
Sachindler, C. (1999). Cytokines and JAK-STAT signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 253:7–14.
Marshall, M.S. (1995). Ras target proteins in eukarotic cells. FASEB J. 9:1311–1318.
Stark, G.R., Kerr, I.M., Williams, B.R.G., Silverman, R.H. and Schreiber, R.D. (1998). How cells respond to interferons. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67:227–264.
Sangfelt, O., Österborg, A., Grander, D., Anderbring, E., Öst, A., Mellstedt, H., et al. (1995). Response to interferon therapy in patients with multiple myeloma correlates with expression of the Bcl-2 oncoprotein. Int. J. Cancer 63:190–192.
Haus, O. (2000). The genes of interferons and interferonrelated factors: localization and relationships with chromosome abberations in cancer. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 48:95–100.
Xu, B., Grander, D., Sangfelt, O. and Einhorn, S. (1994). Primary leukemia cells resistant to IFN-α in vitro are defective in the activation of the DNA-binding factor interferon-stimulated gene factor 3. Blood 84:1942–1949.
Wong, L.H., Krauer, K.G., Hatzinisiriou, I., Estcourt, M.J., Hersey, P., Tam, N.D., et al. (1997). Interferon-resistant human melanoma cells are deficient in ISGF3 components. STAT1, STAT2, and p48-ISGF3γ. J. Biol. Chem. 272:28,779–28,785.
Sun, W.H., Pabon, C., Alsayed, Y., Huang, P.P., Jandeska, S., Uddin, S., et al. (1998). Interferon-α resistance in a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cell line is associated with lack of STAT1 expression. Blood 91:570–576.
Petricoin, E., David, M., Fang, H., Grimley, P., Larner, A.C. and Vande Pol, S. (1994). Human cancer cell lines express a negative transcriptional regulator of the interferon regulatory factor family of DNA binding proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:1477–1486.
Nelson, N., Marks, M.S., Driggers, P.H. and Ozato, K. (1993). Interferon consensus sequence-binding protein, a member of the interferon regulatory factor family, suppresses interferon-induced gene transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13:588–599.
Sakamoto, H., Yasukawa, H., Masuhara, M., Tanimura, S., Sasaki, A., Yuge, K., et al. (1998). A Janus kinase inhibitor, JAB, is an interferon-γ inducible gene and confers resistance to interferons. Blood 92:1668–1676.
Rosenblum, M.G., Maxwell, B.L., Talpaz, M., Kelleher, P.J., McCredie, K.B. and Gutterman, J.U. (1986). In vivo sensitivity and resistance of CML cells to IFN-α: correlation with receptor binding and induction of 2′,5′-oligoadenylate synthetase. Cancer Res. 46:4848–4852.
Heyman, M., Nordgren, A., Jeddi-Tehrani, M., Rasool, O., Liu, Y., Grander, D, et al. (1996). A T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia patient with two malignant cell populations carrying different deletions of the p16INK4 gene. Response to interferon-α therapy in one of the subclones. Leukemia 10:909–924.
Foster, G.R. and Finter, N.B. (1998). Are all type I human interferons equivalent? J. Viral Hepat. 5:143–152
Grandér, D., Sangfelt, O. and Erickson, S. (1997). How does interferon exert its cell growth inhibitory effect? Eur. J. Haematol. 59:129–135.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sangfelt, O., Strander, H. Apoptosis and cell growth inhibition as antitumor effector functions of interferons. Med Oncol 18, 3–14 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/MO:18:1:3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MO:18:1:3