[ad_1]
In a examine of one-dimensional electron correlation states on the MTB of monolayer and bilayer MoSe2, a analysis crew discovered that two forms of correlated insulating states pushed by a dubbed Hubbard-type Coulomb blockade impact may very well be switched by tip pulses.
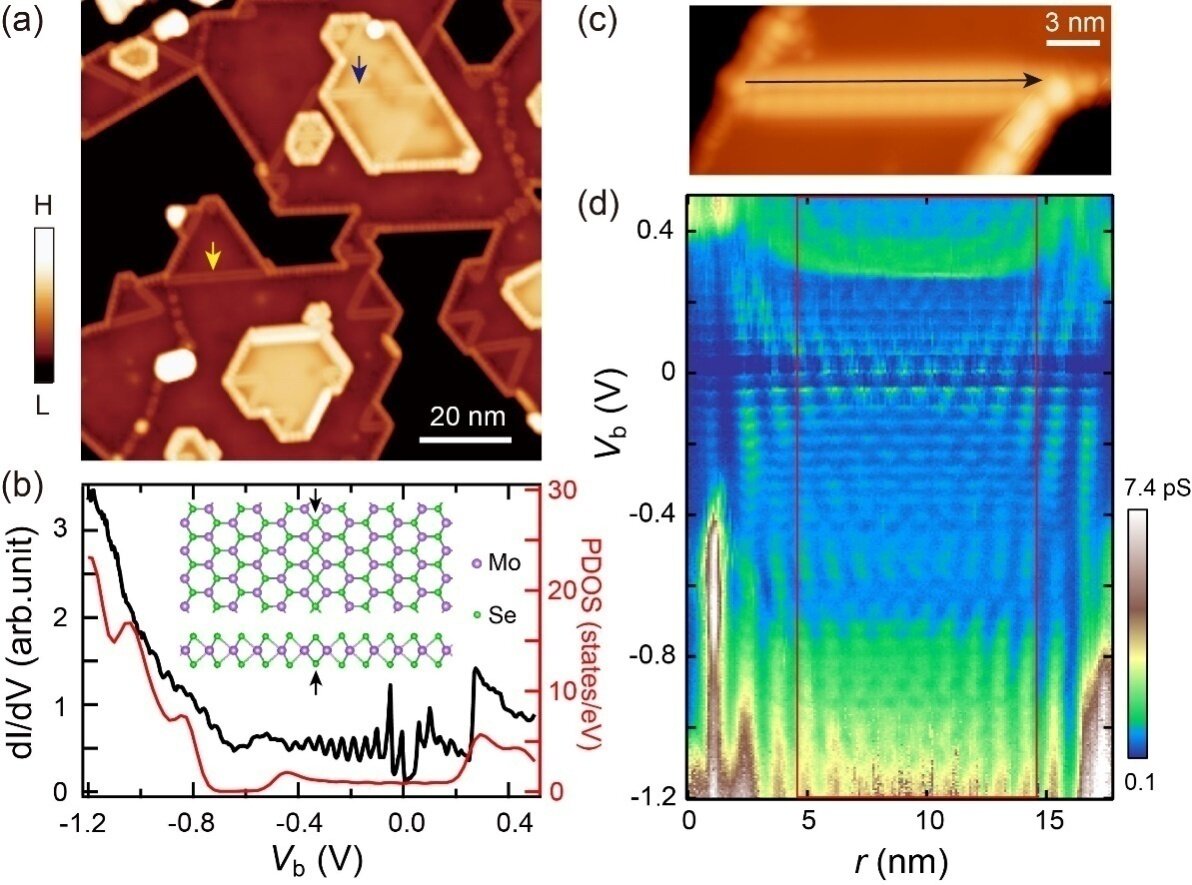
By way of molecular beam epitaxy, this crew has grown single-layer and double-layer MoSe2 movies with one-dimensional MTB on graphene substrates. It’s discovered by scanning tunneling microscopy that the one-dimensional MTB has metallic states. On account of its restricted size, the one-dimensional states are topic to quantum confinement impact, leading to quantized discrete vitality ranges.
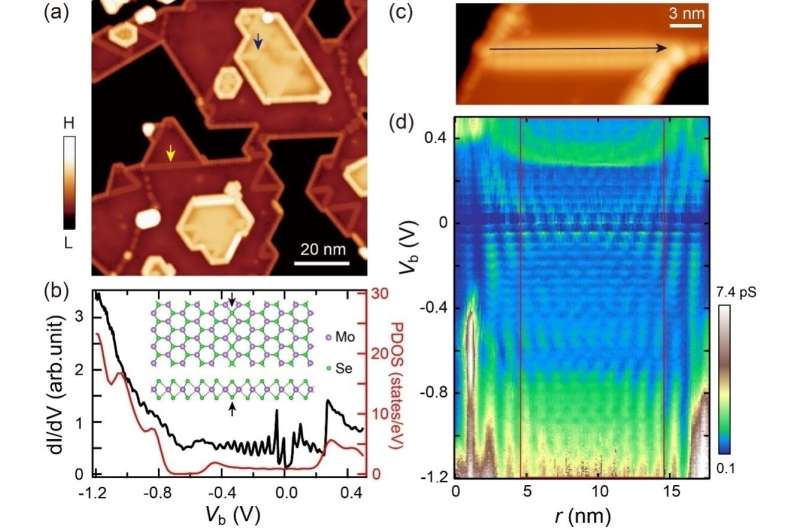
They discovered two forms of MTBs with totally different floor states, outlined as in-phase and out-of-phase states respectively, based on the spatially modulated part of the 2 discrete ranges spanning the Fermi floor. Extra curiously, by making use of tip pulses, it’s attainable to reversibly swap the 2 states.
They confirmed that the Coulomb energies, decided by the wire size, drive the MTB into two forms of floor states with distinct respective cost orders. The quantum nicely states on the Fermi floor are affected by the Coulomb impact.
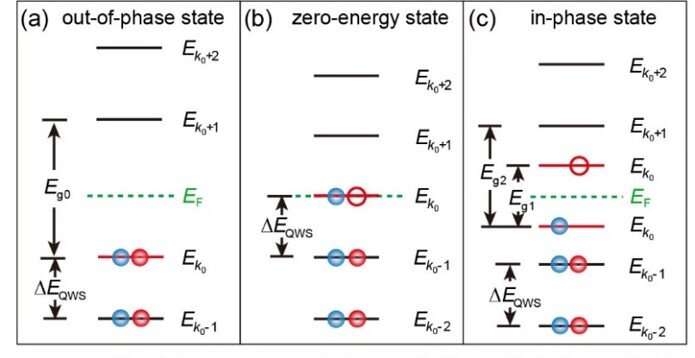
When the Fermi floor is between two quantum-well states with totally different wave vectors, that’s, the out-of-phase state, the vitality stage interval will increase and turns into the sum of Coulomb vitality and the interval of the quantum nicely states.
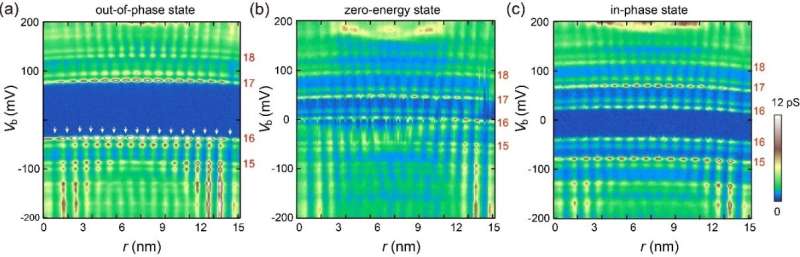
When a quantum nicely is strictly on the Fermi floor, that’s, the in-phase state, the vitality stage is spin–break up by Coulomb vitality to type a single electron occupation, and the splitting dimension is the Coulomb vitality.
The electron filling of MTB is tuned with the tip pulse, the place the extra injected costs, as substantiated by first-principle calculations, are stabilized by way of a polaronic course of, rendering it possible to controllably alter its variety of electrons and its spin state.
The decided Coulomb energies are discovered to solely rely on the wire size, no matter the space of the MTB to the graphene substrate, demonstrating the Coulomb interplay is short-range. That is totally different from the classical Coulomb blockade impact, the place the Coulomb vitality relies on its capacitance to the surroundings and is thus lengthy vary.
Such short-range Coulomb vitality has an identical expression to the classical Coulomb blockade impact, and is thus dubbed Hubbard-type Coulomb blockade impact.
This analysis crew achieved management of electron correlation and spin states on the atomic scale, laying a basis for understanding and tailoring correlated physics in advanced programs.
The analysis was printed in Nationwide Science Evaluation.
Xing Yang et al, Manipulating Hubbard-type Coulomb blockade impact of metallic wires embedded in an insulator, Nationwide Science Evaluation (2022). DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwac210
Quotation:
A Hubbard-type Coulomb blockade impact found within the mirror twin boundary of MoSe₂ (2022, October 28)
retrieved 29 October 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-10-hubbard-type-coulomb-blockade-effect-mirror.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.
[ad_2]